- Afrikaans
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Arabic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Basque
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Catalan
- Cebuano
- China
- China (Taiwan)
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Czech
- Danish
- Dutch
- English
- Esperanto
- Estonian
- Finnish
- French
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- German
- Greek
- Gujarati
- Haitian Creole
- hausa
- hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hindi
- Miao
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- igbo
- Indonesian
- irish
- Italian
- Japanese
- Javanese
- Kannada
- kazakh
- Khmer
- Rwandese
- Korean
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Lao
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembourgish
- Macedonian
- Malgashi
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Myanmar
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Norwegian
- Occitan
- Pashto
- Persian
- Polish
- Portuguese
- Punjabi
- Romanian
- Russian
- Samoan
- Scottish Gaelic
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Spanish
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Swedish
- Tagalog
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Tatar
- Telugu
- Thai
- Turkish
- Turkmen
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uighur
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Bantu
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
Aug . 09, 2024 03:35 Back to list
Designing Efficient Heat Exchangers for Enhanced Thermal Performance in Various Applications
Understanding Heat Exchangers Principles and Applications
Heat exchangers are critical components in various industries, facilitating the transfer of thermal energy between two or more fluids. They play a vital role in improving energy efficiency, ensuring optimal thermal management, and enhancing the overall performance of systems ranging from power plants and chemical processing facilities to residential heating and cooling systems.
Basic Principles of Heat Exchange
The fundamental principle behind a heat exchanger is the second law of thermodynamics, which states that heat flows naturally from a hotter object to a cooler one. In a heat exchanger, two fluids—one hot and one cold—flow in close proximity to each other, allowing thermal energy to be transferred from the hot fluid to the cold fluid without mixing the two. The efficiency of this process is determined by the surface area of the heat exchange surface, the temperature difference between the two fluids, and the heat transfer coefficients of the fluids involved.
There are several types of heat exchangers, each designed for specific applications and operating conditions. The most common types are
1. Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger Consisting of a series of tubes, one set carries the hot fluid while the other carries the cold fluid. The design allows for a large surface area for heat transfer while occupying a relatively small footprint.
2. Plate Heat Exchanger Made up of multiple thin plates arranged to create channels for the two fluids. This design enhances the surface area further and provides excellent heat transfer efficiency, making it ideal for applications requiring tight space constraints.
3. Air Cooled Heat Exchanger This type uses air to cool or heat a fluid. They are particularly useful in locations with limited water availability and are commonly found in power plants and refineries.
4. Double-Pipe Heat Exchanger A simple design where one pipe is placed inside another. It is often used for low-capacity applications due to its straightforward construction and ease of maintenance.
Applications of Heat Exchangers
Heat exchangers are omnipresent in numerous sectors
drawing heat exchanger
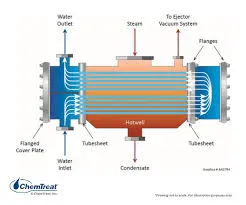
- Power Generation In thermal power plants, heat exchangers are employed to transfer heat from the combusted fuel to water to create steam, which drives turbines for electricity generation
.- Chemical Processing Industries utilize heat exchangers to recover heat from process streams, improving overall energy efficiency and reducing operational costs.
- HVAC Systems In heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems, heat exchangers help maintain comfortable indoor temperatures by efficiently transferring heat between the air and refrigerant units.
- Automotive Industry In vehicles, heat exchangers (like radiators) play a critical role in engine cooling, ensuring the engine operates within a safe temperature range.
Challenges and Considerations
While heat exchangers are essential for efficient thermal energy transfer, several challenges must be addressed
- Fouling Over time, heat exchanger surfaces can become fouled with deposits that reduce their efficiency. Regular maintenance and cleaning are necessary to mitigate this issue.
- Material Selection The choice of materials for heat exchangers is crucial, especially when working with corrosive fluids or high-temperature applications. Using the right material can enhance the lifespan and reliability of the system.
- Design Optimization Engineers must carefully consider factors such as flow rates, pressure drops, and heat transfer coefficients during the design process to maximize performance while minimizing costs.
Conclusion
Heat exchangers are indispensable in modern engineering and industrial applications. As technology advances, the design and efficiency of heat exchangers continue to improve, leading to significant energy savings and environmental benefits. Understanding their principles, types, and applications helps industries harness their potential effectively, paving the way for sustainable practices in energy management and thermal control. Whether in large-scale operations or everyday conveniences, the significance of heat exchangers cannot be overstated.
-
8mm Thin-Walled Cast Steel Manhole Cover Pallet Bottom Ring | Durable
NewsAug.04,2025
-
Premium Cast Iron Water Main Pipe: Durable, Corrosion-Resistant
NewsAug.03,2025
-
Durable Cast Iron Water Mains | AI-Optimized Systems
NewsAug.02,2025
-
High-Efficiency Propane Boiler for Baseboard Heat | Save Energy
NewsAug.01,2025
-
Premium Source Suppliers for Various Gray Iron Castings
NewsJul.31,2025
-
Durable Cast Iron Water Main Pipes | Long-Lasting
NewsJul.31,2025


