- Afrikaans
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Arabic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Basque
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Catalan
- Cebuano
- China
- China (Taiwan)
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Czech
- Danish
- Dutch
- English
- Esperanto
- Estonian
- Finnish
- French
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- German
- Greek
- Gujarati
- Haitian Creole
- hausa
- hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hindi
- Miao
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- igbo
- Indonesian
- irish
- Italian
- Japanese
- Javanese
- Kannada
- kazakh
- Khmer
- Rwandese
- Korean
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Lao
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembourgish
- Macedonian
- Malgashi
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Myanmar
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Norwegian
- Occitan
- Pashto
- Persian
- Polish
- Portuguese
- Punjabi
- Romanian
- Russian
- Samoan
- Scottish Gaelic
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Spanish
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Swedish
- Tagalog
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Tatar
- Telugu
- Thai
- Turkish
- Turkmen
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uighur
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Bantu
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
Nov . 18, 2024 10:15 Back to list
high pressure heat exchanger
High Pressure Heat Exchangers An Essential Component in Modern Industrial Applications
Heat exchangers are pivotal devices used in a variety of industries to transfer heat between two or more fluids. Among the many types of heat exchangers, high pressure heat exchangers are particularly critical in applications involving rigorous temperature and pressure conditions. Their efficient operation is fundamental in industries such as power generation, chemical processing, and aerospace engineering, where they help to enhance energy efficiency and optimize operational performance.
What is a High Pressure Heat Exchanger?
A high pressure heat exchanger is designed to operate under elevated pressure conditions, enabling it to handle fluids that can be in gaseous or liquid states at high temperatures. These exchangers are constructed with robust materials that withstand significant mechanical stresses and corrosion, ensuring durability and integrity even in harsh environments. Common materials used include stainless steel, titanium, and special alloys that offer both strength and resistance to corrosive substances.
Working Principle
The basic principle of heat exchange involves the transfer of thermal energy from a hot fluid to a cooler one. In high pressure systems, this process occurs while maintaining the integrity of the fluids and preventing any unwanted phase changes that could compromise system performance. The heat exchanger consists of various components, including tubes, shells, and fins, strategically designed to maximize surface area and enhance heat transfer efficiency.
The two main types of high pressure heat exchangers are shell-and-tube and plate heat exchangers. Shell-and-tube units consist of a series of tubes, one set carrying the hot fluid and the other the cold fluid, while plate heat exchangers utilize a series of thin plates stacked together. Each has its advantages, with shell-and-tube systems generally suited for larger flow rates and higher pressure applications, whereas plate heat exchangers provide better thermal performance at smaller scales.
Applications in Industry
High pressure heat exchangers find their application across various sectors
high pressure heat exchanger
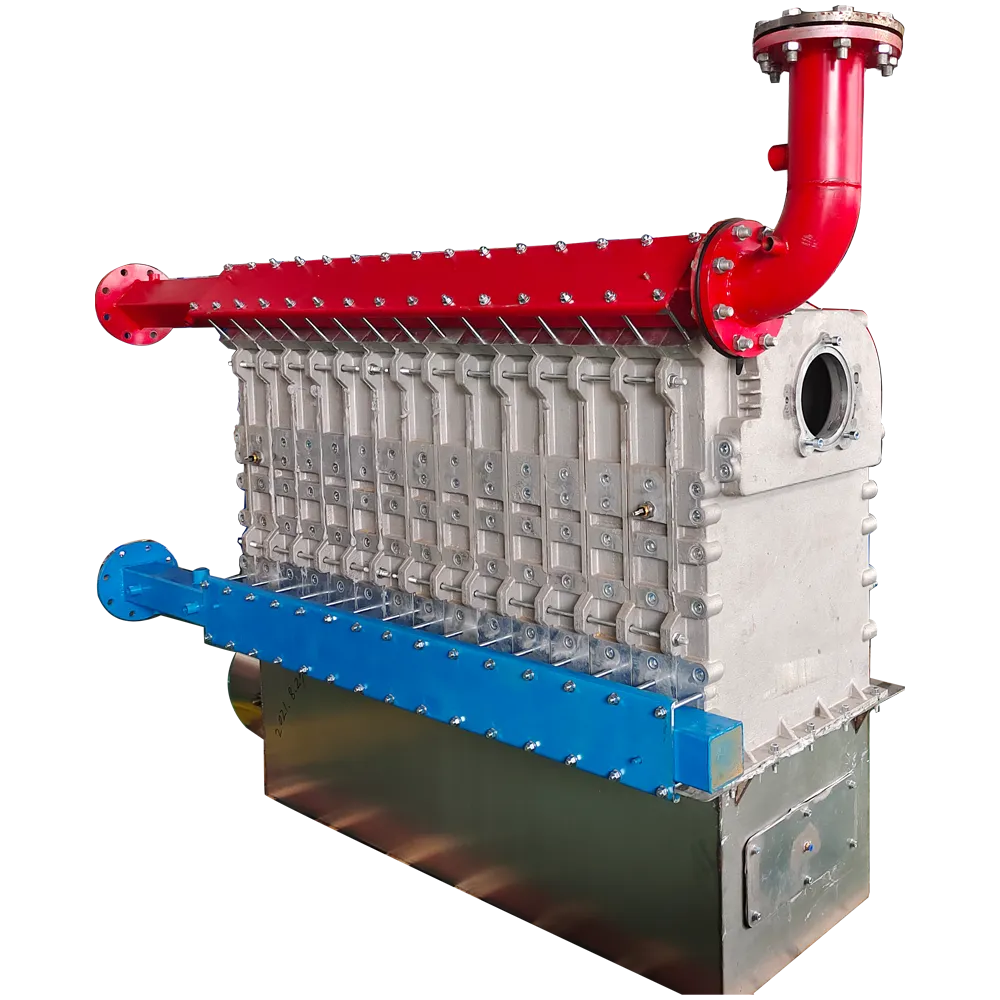
1. Power Generation In power plants, they are crucial for recovering waste heat from exhaust gases or hot fluids, enhancing overall thermal efficiency and reducing emissions.
2. Petrochemical Industry These exchangers are vital in processes such as distillation, where they help in managing heat between different stages, ensuring optimal temperatures for reactions and separations.
3. HVAC Systems In heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC), high pressure heat exchangers are used to recover and reuse heat, contributing to energy savings in large commercial buildings.
4. Marine Applications In shipbuilding and submarine industries, they manage heat in propulsion systems and help maintain comfortable temperatures for crew and equipment.
Challenges and Considerations
Operating at high pressures presents unique challenges. The design and fabrication of these heat exchangers must comply with stringent regulatory and safety standards to prevent catastrophic failures. Engineers must consider factors such as pressure drop, material fatigue, and thermal shock during the design phase. Regular maintenance is also critical to ensure long-term reliability, as fouling and corrosion can significantly impede performance.
Conclusion
High pressure heat exchangers are indispensable in the modern industrial landscape, playing a vital role in maximizing energy efficiency and facilitating complex processes across various applications. The continuous advancement in materials science and engineering techniques promises to enhance their durability and performance, making them even more effective in managing heat transfer under challenging conditions. As industries strive for greater sustainability and efficiency, high pressure heat exchangers will undoubtedly remain at the forefront of technological innovations, helping to meet the demands of an ever-evolving industrial world.
-
8mm Thin-Walled Cast Steel Manhole Cover Pallet Bottom Ring | Durable
NewsAug.04,2025
-
Premium Cast Iron Water Main Pipe: Durable, Corrosion-Resistant
NewsAug.03,2025
-
Durable Cast Iron Water Mains | AI-Optimized Systems
NewsAug.02,2025
-
High-Efficiency Propane Boiler for Baseboard Heat | Save Energy
NewsAug.01,2025
-
Premium Source Suppliers for Various Gray Iron Castings
NewsJul.31,2025
-
Durable Cast Iron Water Main Pipes | Long-Lasting
NewsJul.31,2025


