Feb . 14, 2025 14:44 Back to list
make your own heat exchanger
Creating your own heat exchanger can be a rewarding experience, offering both the satisfaction of a DIY project and the practical benefits of a customized solution for your heating or cooling needs. A deep dive into this venture not only requires some technical know-how but also brings forth the importance of understanding the multiple types of heat exchangers and their specific applications.
As you embark on this project, it is important to adopt standard industry practices in documentations such as maintaining an assembly manual or a specification sheet. This would include detailed information regarding the dimensions, assembly procedures, material specifications, and any other pertinent data. Such meticulous documentation not only enhances the authoritativeness of your project but also serves as a valuable resource for future modifications or troubleshooting. In sharing your experience and insights derived from this endeavor, it's vital to emphasize the importance of iterative prototyping and testing. Slight modifications can often lead to significant improvements in performance, showcasing your expertise as you refine the design for optimal operation. Networking with professionals in the field, engaging in forums, or participating in DIY communities can further enhance your proficiency. These platforms provide an avenue for discussing challenges, exploring innovative solutions, and establishing yourself as a credible and authoritative figure in the engineering community. Lastly, maintaining safety and environmental standards should always be a priority. Adhering to the regulatory requirements not only ensures user safety but also adds a layer of trustworthiness to your project. Informing others about these considerations highlights your commitment to responsible and sustainable engineering practices. In conclusion, the journey of designing and building your own heat exchanger encompasses a blend of technical knowledge, attention to detail, and a commitment to safety protocols. By following these guidelines and sharing your comprehensive knowledge with the community, you contribute to a growing repository of expertise and establish yourself as an authoritative figure in the field of heat exchanger design.
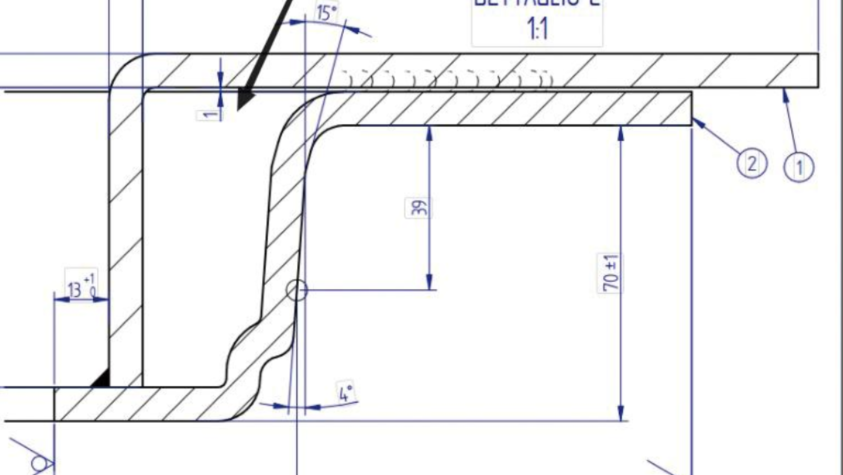

As you embark on this project, it is important to adopt standard industry practices in documentations such as maintaining an assembly manual or a specification sheet. This would include detailed information regarding the dimensions, assembly procedures, material specifications, and any other pertinent data. Such meticulous documentation not only enhances the authoritativeness of your project but also serves as a valuable resource for future modifications or troubleshooting. In sharing your experience and insights derived from this endeavor, it's vital to emphasize the importance of iterative prototyping and testing. Slight modifications can often lead to significant improvements in performance, showcasing your expertise as you refine the design for optimal operation. Networking with professionals in the field, engaging in forums, or participating in DIY communities can further enhance your proficiency. These platforms provide an avenue for discussing challenges, exploring innovative solutions, and establishing yourself as a credible and authoritative figure in the engineering community. Lastly, maintaining safety and environmental standards should always be a priority. Adhering to the regulatory requirements not only ensures user safety but also adds a layer of trustworthiness to your project. Informing others about these considerations highlights your commitment to responsible and sustainable engineering practices. In conclusion, the journey of designing and building your own heat exchanger encompasses a blend of technical knowledge, attention to detail, and a commitment to safety protocols. By following these guidelines and sharing your comprehensive knowledge with the community, you contribute to a growing repository of expertise and establish yourself as an authoritative figure in the field of heat exchanger design.
Share
Pervious:
Latest news
-
Centrifugally Cast Iron Water Main Pipe for Reliable Mains
NewsAug.22,2025
-
Durable Centrifugally Cast Iron Water Main Pipe
NewsAug.11,2025
-
Centrifugally Cast Iron Water Main Pipes for Reliability
NewsAug.10,2025
-
High-Quality Centrifugally Cast Iron Water Main Pipes
NewsAug.09,2025
-
Durable Cast Iron Water Main Pipe & Drainage Solutions
NewsAug.08,2025
-
Buy Cast Iron Pipe: Premium Ductile Iron & Drain Solutions
NewsAug.07,2025


