- Afrikaans
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Arabic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Basque
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Catalan
- Cebuano
- China
- China (Taiwan)
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Czech
- Danish
- Dutch
- English
- Esperanto
- Estonian
- Finnish
- French
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- German
- Greek
- Gujarati
- Haitian Creole
- hausa
- hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hindi
- Miao
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- igbo
- Indonesian
- irish
- Italian
- Japanese
- Javanese
- Kannada
- kazakh
- Khmer
- Rwandese
- Korean
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Lao
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembourgish
- Macedonian
- Malgashi
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Myanmar
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Norwegian
- Occitan
- Pashto
- Persian
- Polish
- Portuguese
- Punjabi
- Romanian
- Russian
- Samoan
- Scottish Gaelic
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Spanish
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Swedish
- Tagalog
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Tatar
- Telugu
- Thai
- Turkish
- Turkmen
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uighur
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Bantu
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
Oct . 13, 2024 15:01 Back to list
Understanding the Functionality and Design of Wall Heat Exchangers in Industrial Applications
Understanding Wall Heat Exchangers Principles and Applications
Heat exchangers play a critical role in various industrial processes, facilitating the efficient transfer of heat between two or more fluids. Among the various types of heat exchangers, wall heat exchangers stand out due to their unique design and functionality. This article explores the principles, advantages, and applications of wall heat exchangers.
What are Wall Heat Exchangers?
Wall heat exchangers, also known as plate or shell-and-tube heat exchangers, consist of a series of plates or tubes that create a barrier between two different fluids typically, a hot fluid and a cold one. The wall acts as a conduit for heat transfer, allowing thermal energy to flow from the hot fluid to the cold fluid without direct mixing. This is particularly advantageous in applications where fluid contamination must be avoided.
Principles of Heat Exchange
The fundamental principle of a wall heat exchanger is based on the laws of thermodynamics. When a hot fluid passes through one side of the heat exchanger, it transfers its thermal energy to the cooler fluid on the opposite side through the wall. This process occurs due to the temperature gradient between the two fluids, with heat naturally flowing from the higher temperature to the lower temperature region.
The efficiency of a wall heat exchanger can be influenced by several factors, including the temperature difference between the fluids, the flow arrangement (counterflow, parallel flow, or crossflow), and the materials used for the wall. Counterflow configurations, where the two fluids move in opposite directions, are often the most efficient, as they maintain a higher temperature gradient across the entire length of the heat exchanger.
Advantages of Wall Heat Exchangers
1. Efficiency Wall heat exchangers are known for their high thermal efficiency. Due to their design, they can effectively transfer heat with a minimal temperature drop, maximizing energy recovery.
2. Space Optimization Their compact design allows for a reduced footprint, which is particularly beneficial in applications where space is limited. This characteristic also translates into lower installation costs.
3. Versatility Wall heat exchangers can handle a variety of fluids, including gases, liquids, and even slurries, making them suitable for diverse applications in industries such as power generation, chemical processing, and HVAC systems.
wall heat exchanger
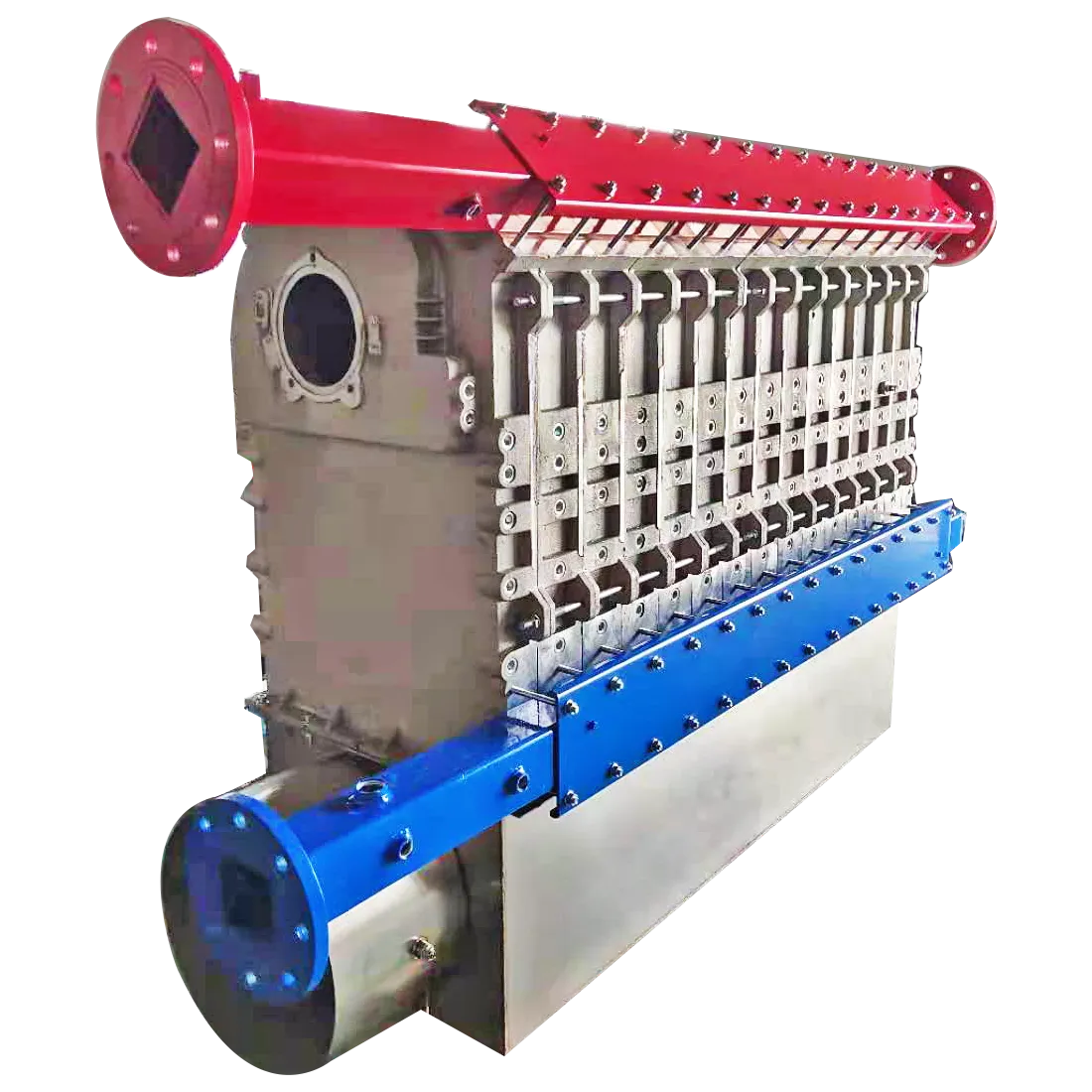
4. Ease of Maintenance Depending on the specific design, wall heat exchangers can be relatively easy to clean and maintain. Many models are designed to be disassembled, allowing for thorough inspections and servicing.
Applications of Wall Heat Exchangers
Wall heat exchangers find applications in a wide array of industries
- Chemical Processing Used for cooling or heating reactants in chemical reactors, thus enhancing reaction rates and product yields.
- Power Generation Essential in condensers and cooling systems, they help maintain optimal operating temperatures for turbines and other machinery.
- HVAC Systems Wall heat exchangers are critical in heating and cooling systems, including district heating and cooling applications, where they regulate building temperatures efficiently.
- Food and Beverage Industry In pasteurization processes, wall heat exchangers provide effective heat treatment while ensuring product safety and quality.
- Petrochemical Industry Used in various processes, including heat recovery from flue gases and in crude oil processing.
Conclusion
Wall heat exchangers represent a vital technology in thermal management across various sectors. Their ability to transfer heat efficiently while maintaining the necessary separation between fluids makes them indispensable in numerous applications. As industries continue to seek ways to optimize energy usage and reduce operational costs, the role of wall heat exchangers is likely to expand even further, contributing to more sustainable and efficient processes. Understanding their principles and advantages will enable engineers and designers to implement these systems effectively, leading to improved overall efficiency in heat transfer operations.
-
Premium Cast Iron Water Main Pipe: Durable, Corrosion-Resistant
NewsAug.03,2025
-
Durable Cast Iron Water Mains | AI-Optimized Systems
NewsAug.02,2025
-
High-Efficiency Propane Boiler for Baseboard Heat | Save Energy
NewsAug.01,2025
-
Premium Source Suppliers for Various Gray Iron Castings
NewsJul.31,2025
-
Durable Cast Iron Water Main Pipes | Long-Lasting
NewsJul.31,2025
-
High-Quality Cast Iron Water Main Pipe for Durable Infrastructure
NewsJul.30,2025


